Insulin resistance is a condition where your body’s cells become resistant to the effects of insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas that helps regulate blood sugar levels. When cells resist insulin, glucose accumulates in the bloodstream, leading to various health issues. Recognizing the signs of insulin resistance is crucial for early detection and management.
Insulin resistance, a condition where the body’s cells become less responsive to insulin, has profound implications for health, longevity, and overall quality of life. When the body fails to effectively use insulin, blood sugar levels rise, increasing the risk of type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and obesity.
Moreover, insulin resistance is often associated with inflammation and metabolic dysfunction, which can lead to a host of other health issues such as high blood pressure, elevated cholesterol levels, and even certain cancers. Over time, these health complications can significantly reduce life expectancy and diminish overall quality of life, highlighting the critical importance of addressing insulin resistance through lifestyle changes, medication, and proper medical management.
15 signs your body may be showing that could indicate insulin resistance:
●Persistent Fatigue: Feeling constantly tired or fatigued, even after getting enough rest, could be a sign of insulin resistance. Fluctuating blood sugar levels can disrupt energy levels and leave you feeling drained.
●Increased Hunger: Experiencing frequent hunger or intense cravings, especially for sugary or carbohydrate-rich foods, may indicate insulin resistance. This occurs as the body struggles to regulate blood sugar levels, leading to increased appetite.
●Weight Gain, Especially Around the Abdomen: Insulin resistance is closely linked to weight gain, particularly in the abdominal area. This visceral fat accumulation is a key indicator of metabolic disturbances.
●High Blood Pressure: Hypertension or high blood pressure often coexists with insulin resistance. The mechanisms underlying both conditions are interrelated and can exacerbate each other.
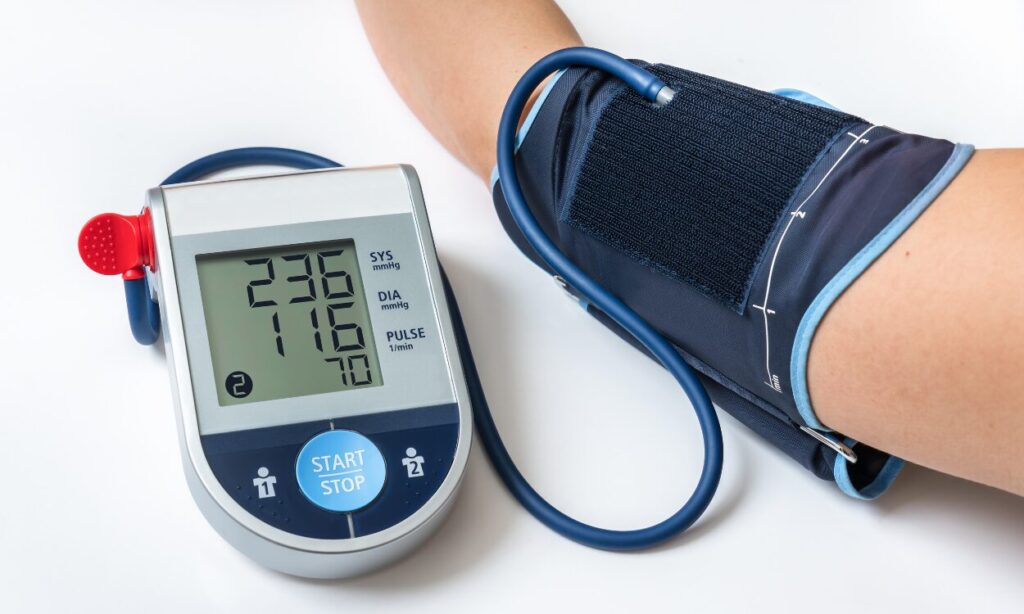
●Frequent Urination: Insulin resistance can lead to excess glucose in the bloodstream, prompting the kidneys to work harder to filter and excrete it. This may result in increased urination, particularly during the night (nocturia).
●Increased Thirst: Excessive thirst (polydipsia) is another common symptom of insulin resistance. It occurs as a response to dehydration caused by frequent urination.
●Skin Changes: Dark patches of skin, especially around the neck, armpits, or other areas with folds or creases (acanthosis nigricans), can indicate insulin resistance. This condition is often associated with obesity and type 2 diabetes.
●Frequent Infections: Insulin resistance can weaken the immune system, making you more susceptible to infections, particularly fungal infections like yeast infections (e.g., thrush) and skin infections.
●Slow Wound Healing: Impaired insulin function can hinder the body’s ability to heal wounds and injuries. If you notice that cuts or bruises take longer than usual to heal, it may be a sign of insulin resistance.
●Brain Fog: Cognitive issues such as difficulty concentrating, memory problems, or mental fog can occur due to fluctuating blood sugar levels associated with insulin resistance.
●Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): Women with insulin resistance are at a higher risk of developing PCOS, a hormonal disorder characterized by irregular menstrual cycles, ovarian cysts, and symptoms like acne and hirsutism (excessive hair growth).
●Erectile Dysfunction: Men with insulin resistance may experience difficulties achieving or maintaining an erection due to compromised blood flow and nerve function caused by high blood sugar levels.
●Sleep Problems: Insulin resistance can disrupt sleep patterns, leading to insomnia, sleep apnea, or other sleep disorders. Poor sleep quality further exacerbates insulin resistance and metabolic dysfunction.
●Mood Swings: Fluctuations in blood sugar levels can affect neurotransmitter function, contributing to mood swings, irritability, anxiety, or depression.
●High Triglyceride Levels: Insulin resistance often coexists with dyslipidemia, characterized by elevated levels of triglycerides and low levels of HDL cholesterol, increasing the risk of cardiovascular disease.
Recognizing these signs of insulin resistance is crucial for early intervention and prevention of associated health complications. If you experience multiple symptoms or have risk factors such as obesity, family history of diabetes, or sedentary lifestyle, consult a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and management.
FAQs
What is insulin resistance?
Insulin resistance is a condition where cells become less responsive to insulin, leading to elevated blood sugar levels. It’s a precursor to type 2 diabetes and is associated with various health complications.
What causes insulin resistance?
Insulin resistance can be caused by genetics, obesity, sedentary lifestyle, poor diet (especially high sugar and refined carbohydrate intake), aging, and certain medical conditions.
How is insulin resistance diagnosed?
Insulin resistance is typically diagnosed through blood tests measuring fasting insulin levels, glucose levels, and calculating the Homeostatic Model Assessment of Insulin Resistance (HOMA-IR). Additionally, other metabolic markers and clinical symptoms are considered.
Can insulin resistance be reversed?
Yes, insulin resistance can often be reversed or improved through lifestyle modifications such as regular exercise, healthy diet, weight loss, and medications if necessary.
What are the long-term complications of insulin resistance?
Long-term complications of insulin resistance include type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, hypertension, kidney disease, and neurological issues.
Is insulin resistance only a concern for overweight or obese individuals?
While obesity is a significant risk factor for insulin resistance, it can affect individuals of any weight. Factors such as genetic predisposition, sedentary lifestyle, and poor dietary habits play crucial roles.
Can insulin resistance affect fertility?
Yes, insulin resistance is associated with reproductive issues such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) in women and erectile dysfunction in men, which can impact fertility.
Are there any specific diets recommended for managing insulin resistance?
Diets rich in fiber, lean protein, healthy fats, and low in refined carbohydrates and added sugars are beneficial for managing insulin resistance. Examples include the Mediterranean diet and low glycemic index diet.
Does exercise help with insulin resistance?
Yes, regular physical activity improves insulin sensitivity, helps control blood sugar levels, and reduces the risk of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes.
When should I see a doctor if I suspect insulin resistance?
If you experience symptoms such as excessive thirst, frequent urination, unexplained weight gain, or have risk factors for insulin resistance, it’s advisable to consult a healthcare professional for evaluation, diagnosis, and appropriate management.

