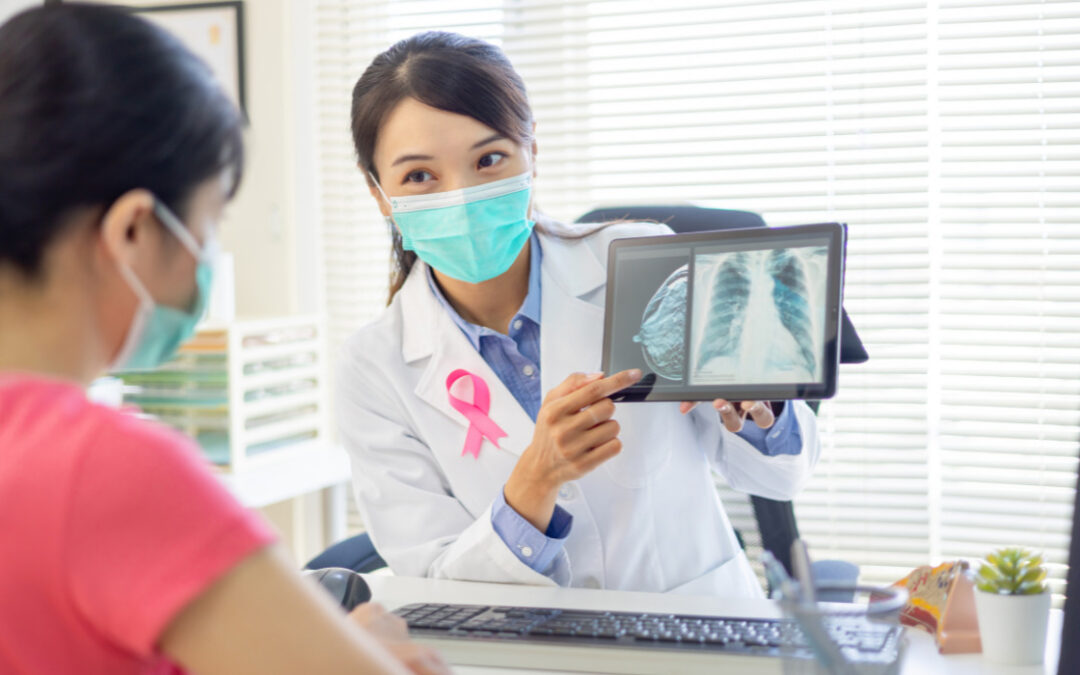
Breast cancer stands as a formidable adversary, impacting the lives of millions worldwide. This comprehensive guide aims to empower individuals by shedding light on the early signs and symptoms of breast cancer, exploring available treatments, and delving into crucial information for navigating this challenging journey.
Understanding Breast Cancer
Breast cancer is a complex condition characterized by the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells in the breast, forming either benign or malignant tumors. Malignant tumors possess the potential to invade surrounding tissues and spread to other parts of the body, making early detection crucial for effective treatment.
Early Signs and Symptoms
Lump in the Breast or Underarm
The most recognizable symptom is the presence of a painless lump or thickening in the breast or underarm. Regular self-examinations, typically recommended for women starting in their 20s, can aid in the early detection of such lumps.
Changes in Breast Size or Shape
Unexplained changes in breast size or shape can be indicative of underlying issues. Regular monitoring of one’s breast appearance can help detect abnormalities.
Skin Changes
Redness, dimpling, or puckering of the skin on the breast may signal an underlying problem. Any changes in skin texture should be promptly addressed.
Nipple Abnormalities
Changes in nipple appearance, such as inversion, discharge, or sudden tenderness, warrant attention. Regular breast self-exams should include an examination of the nipples.
Pain or Discomfort
Persistent pain or discomfort in the breast that is not related to the menstrual cycle should be evaluated by a healthcare professional. While pain does not always indicate cancer, it is essential to rule out potential issues.
Diagnosis
If any of these symptoms are present, it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional promptly. Diagnostic procedures may include mammograms, ultrasounds, and biopsies to confirm the presence of cancer and determine its characteristics.
Types of Breast Cancer
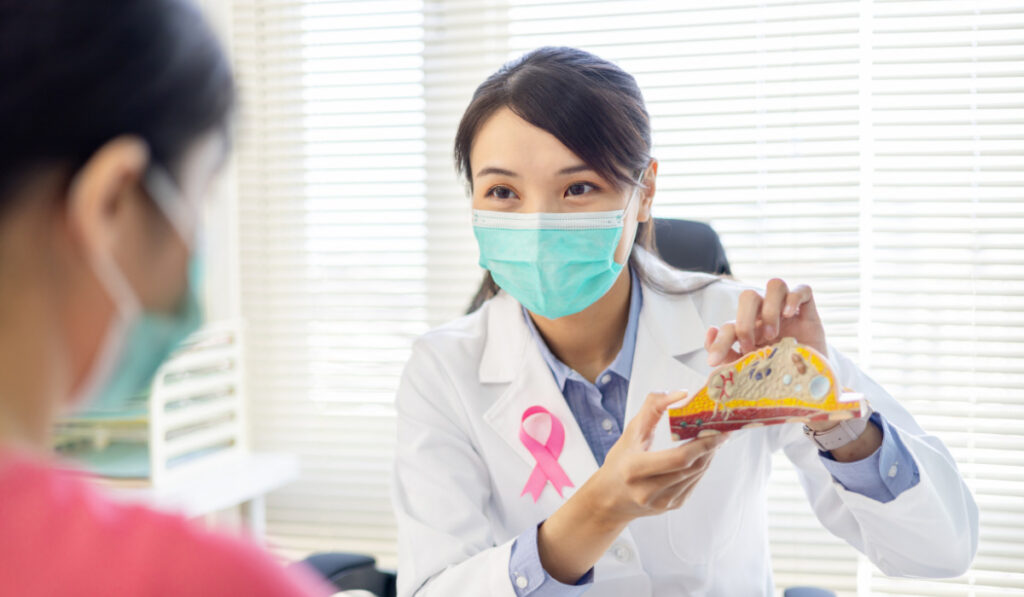

Various types of breast cancer exist, each with distinct characteristics. Common types include ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS), invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC), and invasive lobular carcinoma (ILC). The specific type of breast cancer influences treatment decisions.
Stages of Breast Cancer
Breast cancer staging is a crucial aspect of treatment planning. It considers the size of the tumor, its spread to lymph nodes, and its presence in other parts of the body. Staging helps determine the most appropriate treatment plan, ranging from localized interventions to systemic approaches.
Lump in the left breast is tied to the lymphatic system. Make sure you are moving, doing jumping jacks or ,Jumping trampoline to pump out the waste from the lymphatic system.
Lump in the right breast is connected with liver congestion or emotional trauma during an earlier stage of life and is not resolved. Gallbladder and liver cleanse will help.
Here is the book to read on this.
Treatment Options
Surgery
Surgical interventions, such as lumpectomy or mastectomy, may be recommended depending on the size and stage of the tumor. The goal is to remove the cancerous tissue while preserving as much healthy tissue as possible.
Radiation Therapy
This treatment involves the use of high-energy rays to target cancer cells and reduce the risk of recurrence after surgery. It is often employed in conjunction with surgery or as a standalone treatment.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy utilizes medications to target and destroy rapidly dividing cancer cells throughout the body. It is a systemic treatment that may be administered before or after surgery, depending on the cancer type and stage.
Hormone Therapy
Hormone receptor-positive cancers may benefit from hormone therapy, which aims to block hormones that fuel certain types of breast cancer. This targeted approach helps prevent cancer cells from receiving the signals needed for growth.
Targeted Therapy
Targeted therapy focuses on specific molecules involved in cancer growth. By targeting these molecules, the treatment minimizes damage to healthy cells, leading to more effective and less toxic outcomes.
Survivorship and Support
Survivorship begins once active treatment concludes. This phase involves ongoing medical care, emotional support, and lifestyle adjustments. Support groups, counseling, and a strong social network can contribute significantly to emotional well-being during and after treatment.
Alternative Naturopathic and other options: I am firm believer to attack this with consulting regular medical care as well as natropathic and other life style changed interventions. You are the driver and decisions maker of your health. Get all the information and you decide what to do.
Do not delegate your health care, stay involved and determined and you will fund a way to get Healthy and Stay healthy.
Conclusion
Breast cancer is a challenging journey, but early detection, advancements in treatment, and a robust support system can significantly improve outcomes. Regular screenings, awareness, and a proactive approach to healthcare are pivotal in the fight against breast cancer.
By staying informed and advocating for one’s health, individuals can navigate this journey with resilience and hope, fostering a sense of empowerment throughout the process.
FAQs
What are the risk factors for developing breast cancer?
Breast cancer risk factors include age, family history, genetic mutations (such as BRCA1 and BRCA2), hormonal factors (early menstruation, late menopause), dense breast tissue, personal history of breast cancer or certain non-cancerous breast diseases, and exposure to estrogen-like compounds.
How often should I perform a breast self-exam, and when should I start?
The American Cancer Society recommends monthly breast self-exams starting in your 20s. Therefore while these exams are not a substitute for regular mammograms and clinical breast exams, they empower individuals to become familiar with their breasts and promptly report any changes to their healthcare provider.
Are mammograms the only screening method for breast cancer?
Mammograms are a primary screening tool, but additional methods, such as breast MRI and ultrasound, may be recommended based on individual risk factors or specific symptoms. Moreover regular mammograms are typically advised for women aged 40 and older, but individual screening plans may vary.
How is breast cancer staged, and what does it mean for my treatment?
Breast cancer staging involves determining the extent of the disease. Stages range from 0 to IV, with lower stages indicating localized cancer and higher stages suggesting more widespread disease. Staging guides treatment decisions, helping healthcare professionals tailor interventions to the specific characteristics of the cancer.
What is the role of genetic testing in breast cancer diagnosis and treatment?
Genetic testing, particularly for BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations, can provide valuable information about a person’s predisposition to breast cancer. This information may guide treatment decisions, including the consideration of prophylactic measures and screening for family members.
Is breast cancer only prevalent in women?
While breast cancer is more common in women, men can also develop the disease. Male breast cancer accounts for a small percentage of all breast cancer cases. Symptoms and treatment for breast cancer in men are similar to those in women.
What lifestyle changes can lower the risk of breast cancer?
Adopting a healthy lifestyle can contribute to overall well-being and potentially lower the risk of breast cancer. This includes maintaining a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, limiting alcohol consumption, avoiding smoking, and managing stress.
How can I support a loved one diagnosed with breast cancer?
Supporting a loved one through a breast cancer diagnosis involves being empathetic, offering practical assistance, and providing emotional support. Therefore educate yourself about their treatment plan, attend appointments when possible, and create a supportive environment. Moreover encourage open communication and be mindful of their unique needs throughout the journey.

